classification
Last edited 05/2019
Different proteins can be deposited as amyloid in various tissues
- deposition can be restricted to one specific site (such as pancreas, brain,
larynx) (localized amyloidosis) or can be found throughout the body (systemic
amyloidosis)
- are a many types of localized amyloidosis including cerebral endocrine,
and cutaneous amyloidosis
- only the name amyloid is identical, but the localised types of amyloid
mentioned above are completely different because of different precursor
proteins
- only the name amyloid is identical, but the localised types of amyloid
mentioned above are completely different because of different precursor
proteins
- are a many types of localized amyloidosis including cerebral endocrine,
and cutaneous amyloidosis
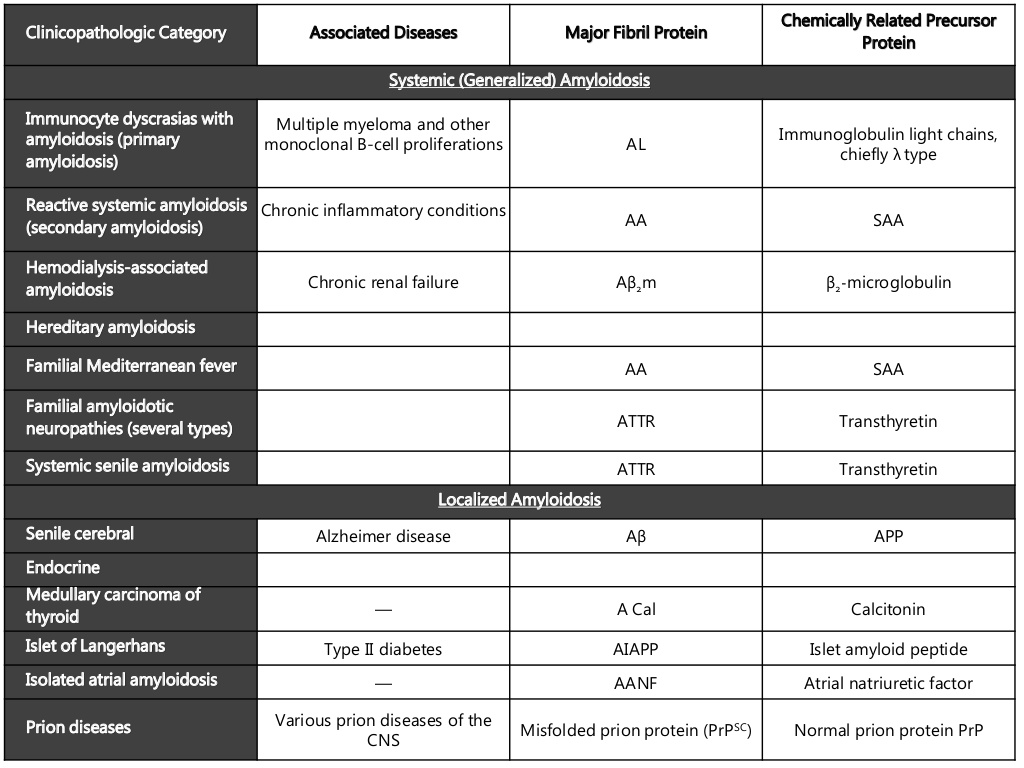
- five main types of systemic amyloidosis are:
- systemic forms of amyloid that should be distinguished from each other
(four acquired and one hereditary) are AA, AL, Aß2M, and two ATTR
types:
- acquired AA amyloidosis
- caused by chronic inflammation
- serum amyloid A protein (SAA), an acute phase reactant, is the precursor protein of this type
- proteinuria and loss of renal function are the most prominent
clinical characteristics
- acquired AL amyloidosis
- caused by a plasma cell dyscrasia
- precursor protein of this type is a kappa or lambda immunoglobulin light chain
- clinical characteristics of this type are very diverse, such as
cardiomyopathy, hepatomegaly, nephrotic syndrome, severe diarrhoea,
carpal tunnel syndrome, and neuropathy (peripheral as well as autonomic
neuropathy)
- acquired Aß2M amyloidosis
- caused by chronic dialysis because of complete renal failure
- precursor protein of this type is ß2-microglobulin because high serum levels are the result of the impossibility to excrete this protein
- clinical characteristics of this type are carpal tunnel syndrome
and joint problems (shoulders, wrists, fingers, hips, vertebral
column, etc.)
- caused by chronic dialysis because of complete renal failure
- acquired ATTR amyloidosis
- found at older age (especially older than 80 years)
- the normal wild type precursor protein transthyretin (TTR) is the characteristic protein
- clinically characterised by a slowly progressive cardiomyopathy
- hereditary ATTR amyloidosis
- caused by more than 80 autosomal dominant hereditary point mutations of the precursor protein transthyretin (TTR)
- clinical characteristics of this type are peripheral and autonomic neuropathy, but also cardiac, renal, and ocular involvement can be seen
- acquired AA amyloidosis
Reference:
- Misumi Y, Ando Y.Classification of amyloidosis. Brain Nerve. 2014 Jul;66(7):731-7.
- Dey A. Classification of Amyloidosis.