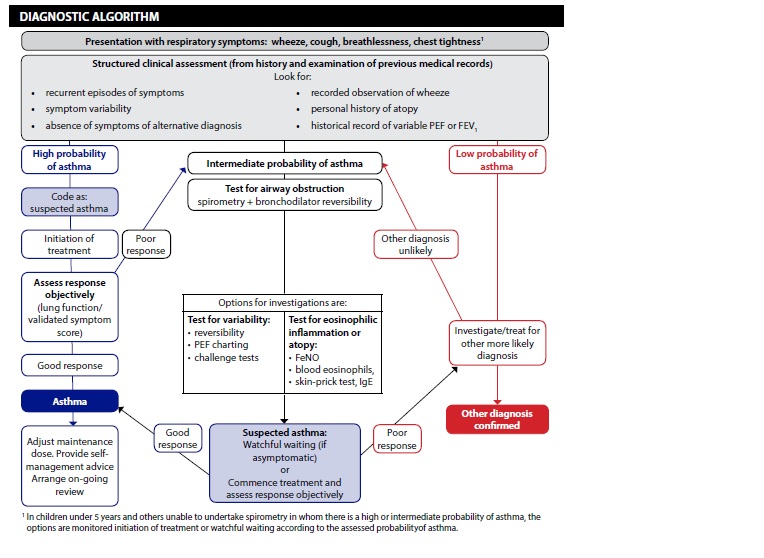
if intermediate probability of asthma
Last edited 11/2019
Intermediate Probability:
Adults and children who have some, but not all, of the typical features of asthma on an initial structured clinical assessment or who do not respond well to a monitored initiation of treatment have an intermediate probability of asthma
Spirometry, with bronchodilator reversibility as appropriate, is the preferred initial test for investigating intermediate probability of asthma in adults, and in children old enough to produce reliable results on testing.
- In adults and children with an intermediate probability of asthma and airways
obstruction identified through spirometry, undertake reversibility tests and/or
a monitored initiation of treatment assessing the response to treatment by
repeating lung function tests and objective measures of asthma control
- In adults and children with an intermediate probability of asthma and normal
spirometry results, undertake challenge tests and/or measurement of FeNO to
identify eosinophilic inflammation
- In children with an intermediate probability of asthma who cannot
perform spirometry:
- consider watchful waiting if the child is asymptomatic
- offer a carefully monitored trial of treatment if the child is symptomatic.
Check for possible occupational asthma by asking employed people with suspected new-onset asthma, or established asthma that is poorly controlled:
- are symptoms better on days away from work?
- are symptoms better when on holiday?
Make sure all answers are recorded for later review (2).
Reference:
further investigation with an intermediate probability of asthma