treatment of pulmonary embolism
Last edited 05/2020
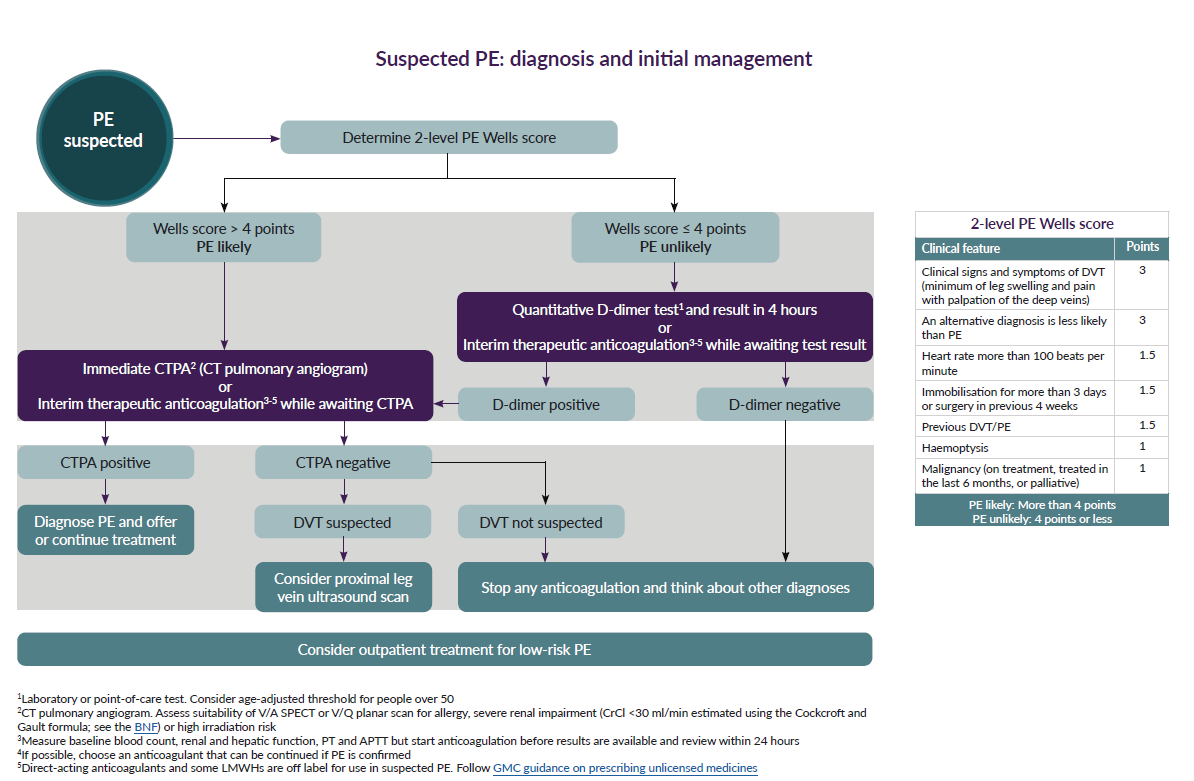
NICE suggest (1):
The task force for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism of the European Society of Cardiology suggest that the severity of PE should be understood according to the PE-related early mortality risk rather than the anatomical burden and the shape and distribution of intrapulmonary emboli (2).
Hence the task force suggests that the currently used terms such as 'massive', 'submassive' and 'non-massive' be replaced with the estimated level of the risk of PE-related early death (during the acute phase in the hospital or within 30 days ) (2).
- initial risk stratification of suspected or confirmed PE, based on the presence of
haemodynamic instability, is recommended to identify patients at high risk of early
mortality
- in patients without haemodynamic instability, further stratification of patients with acute PE
into intermediate- and low-risk categories is recommended
- in patients without haemodynamic instability, use of clinical prediction rules integrating PE
severity and comorbidity, preferably the PESI or sPESI (simplified
Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index) , should be considered for risk
assessment in the acute phase of PE
- assessment of the RV by imaging methodsc or laboratory biomarkersd should be
considered, even in the presence of a low PESI or a negative sPESI
- in patients without haemodynamic instability, use of validated scores combining clinical, imaging, and laboratory PE-related prognostic factors may be considered to further stratify the severity of the acute PE episode
Definition of haemodynamic instability, which delineates acute high-risk pulmonary embolism (one of the following clinical manifestations at presentation)
| Cardiac arrest | Obstructive Shock | Persistent hypotension |
| Need for cardiopulmonary resuscitation | Systolic BP <90 mmHg or vasopressors required And |
Systolic BP <90 mmHg or systolic BP drop >=40 mmHg, lasting longer than 15 min and not caused by new-onset arrhythmia, hypovolaemia, or sepsis |
European guidance defines PE severity and the risk
| High Risk |
is a life threatening condition |
| Intermediate-high Risk |
. |
| Intermediate-low Risk |
|
| Low Risk |
low risk PE - all checked RV dysfunction and myocardial injury markers are found negative, short term PE related mortality is <1% |
key:
BP: blood pressure; CTPA: computed tomography pulmonary angiography; H-FABP:heart-type fatty acid-binding protein; NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide; PE: pulmonary embolism; PESI: Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index; RV: right ventricular; sPESI: simplified Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index; TTE: transthoracic echocardiogram.
(a) One of the following clinical presentations: cardiac arrest, obstructive shock (systolic BP <90 mmHg or vasopressors required to achieve a BP >= 90 mmHg despite an adequate filling status, in combination with end-organ hypoperfusion), or persistent hypotension (systolic BP <90 mmHg or a systolic BP drop >= 40 mmHg for >15 min, not caused by new-onset arrhythmia, hypovolaemia, or sepsis)
(b) Prognostically relevant imaging (TTE or CTPA) findings in patients with acute PE
(c) Elevation of further laboratory biomarkers, such as NT-proBNP >= 600 ng/L, H-FABP >= 6 ng/mL, or copeptin >= 24 pmol/ L, may provide additional prognostic information. These markers have been validated in cohort studies but they have not yet been used to guide treatment decisions in randomized controlled trials
(d) Haemodynamic instability, combined with PE confirmation on CTPA and/or evidence of RV dysfunction on TTE, is sufficient to classify a patient into the high-risk PE category. In these cases, neither calculation of the PESI nor measurement of troponins or other cardiac biomarkers is necessary.
(e) Signs of RV dysfunction on TTE (or CTPA) or elevated cardiac biomarker levels may be present, despite a calculated PESI of I–II or an sPESI of 0.
Recommendations for High Risk PEs - acute treatment (2):
- anticoagulation with UFH, including a weight-adjusted bolus injection, be initiated without delay in patients with high-risk PE
- systemic thrombolytic therapy is recommended for high-risk PE
- surgical pulmonary embolectomy is recommended for patients with high-risk PE, in whom thrombolysis is contraindicated or has failed
- percutaneous catheter-directed treatment should be considered for patients with high-risk PE, in whom thrombolysis is contraindicated or has failed
- norepinephrine and/or dobutamine should be considered in patients with high-risk PE
- ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) may be considered, in combination with surgical embolectomy or catheter-directed treatment, in patients with PE and refractory circulatory collapse or cardiac arrest
Reference:
- NICE (March 2020). Venous thromboembolic diseases: the management of venous thromboembolic diseases and the role of thrombophilia testing
- .Konstantinides SV et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS) The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Respir J. 2019 Oct 9;54(3)
treatment of massive pulmonary embolism
treatment of a medium sized pulmonary embolus
treatment of multiple small emboli
treatment of recurrent pulmonary emboli
recommendations on the diagnostic investigations to be employed in suspected PE
provoked versus unprovoked pulmonary embolism (PE) or deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
inferior vena cava filter with proximal deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE)