edoxaban
Last edited 04/2019
Edoxaban
Consult the SPC before prescribing.
- is a factor Xa inhibitor and is available as 15mg, 30mg and 60mg tablets
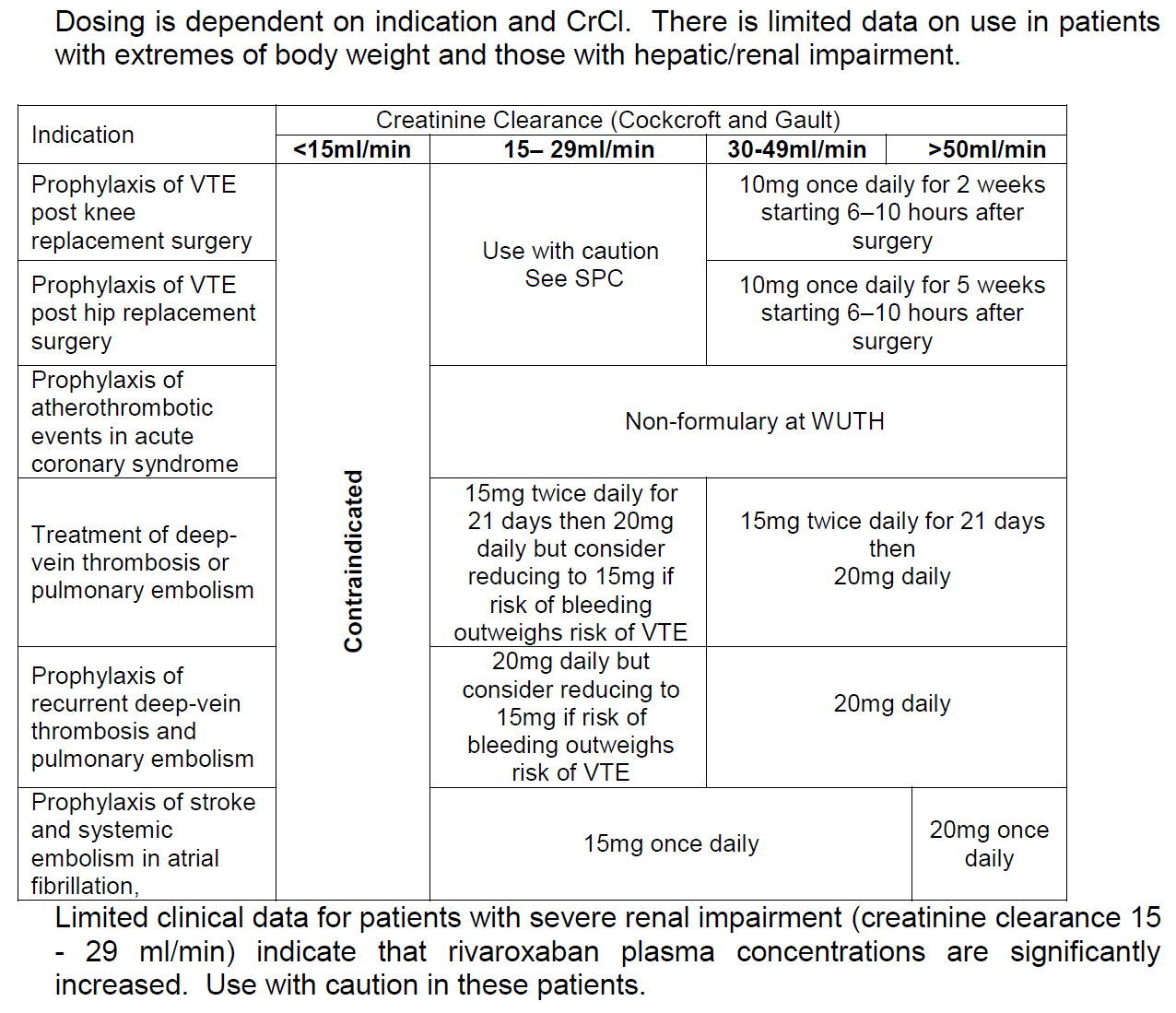
Indications (1,2)
- Stroke prevention in adult patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation
- Treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism and prevention of recurrent DVT and PE in adults
Contra-indications (1,2)
- Clinically significant active bleeding
- Hepatic disease associated with coagulopathy and clinically relevant bleeding risk
- Lesion or condition, if considered to be a significant risk for major bleeding. This may include current or recent gastrointestinal ulceration, presence of malignant neoplasms at high risk of bleeding, recent brain or spinal injury, recent brain, spinal or ophthalmic surgery, recent intracranial haemorrhage, known or suspected oesophageal varices, arteriovenous malformations, vascular aneurysms or major intraspinal or intracerebral vascular abnormalities
- Uncontrolled severe hypertension.
- Concomitant treatment with any other anticoagulants e.g. unfractionated heparin (UFH), low molecular weight heparins, heparin derivatives, oral anticoagulants except under specific circumstances of switching oral anticoagulant therapy or when UFH is given at doses necessary to maintain an open central venous or arterial catheter
- Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Initiation
- Baseline Activated Partial Prothrombin Time (aPTT), International Normalised Ratio(INR), haemoglobin, urea & electrolytes and liver function tests
- Weigh patient and obtain height
- Calculate baseline creatinine clearance (CrCl)
- If switching from another anticoagulant to edoxaban:
- Parenteral anticoagulants to edoxaban - Discontinue parenteral anticoagulant and start edoxaban at the time of the next scheduled dose
- Vitamin K antagonists to edoxaban VKA treatment should be stopped and edoxaban therapy should be initiated when the INR is <=2.5
- If switching from edoxaban to VKA then refer to SPC for full information
Reference:
- Wirral University Teaching Hospital NHS Trust. Oral Anticoagulants (VKA and DOAC) Guidelines for prescribing, monitoring and management (Accessed 23/4/19)
- NHS Specialist Pharmacy Service (October 2017). Suggestions for Drug Monitoring in Adults in Primary Care